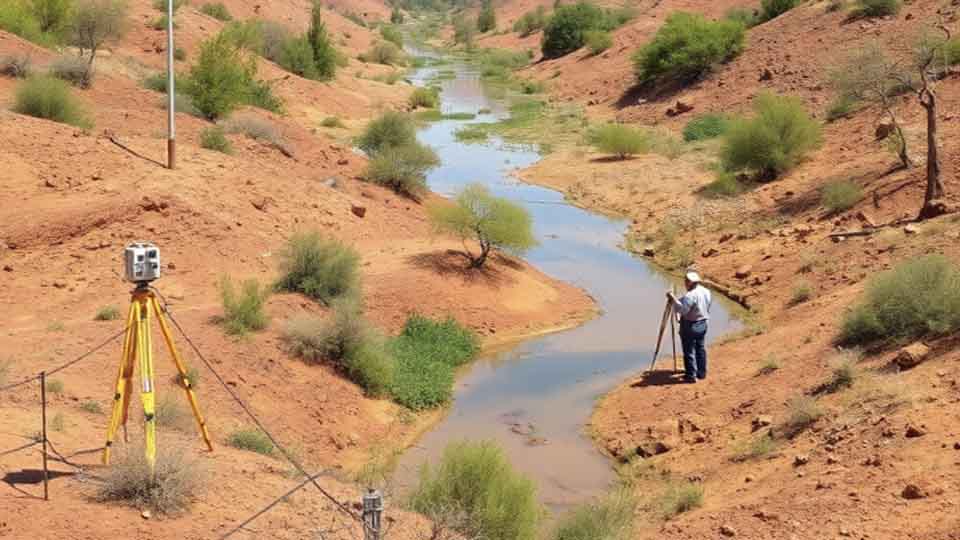
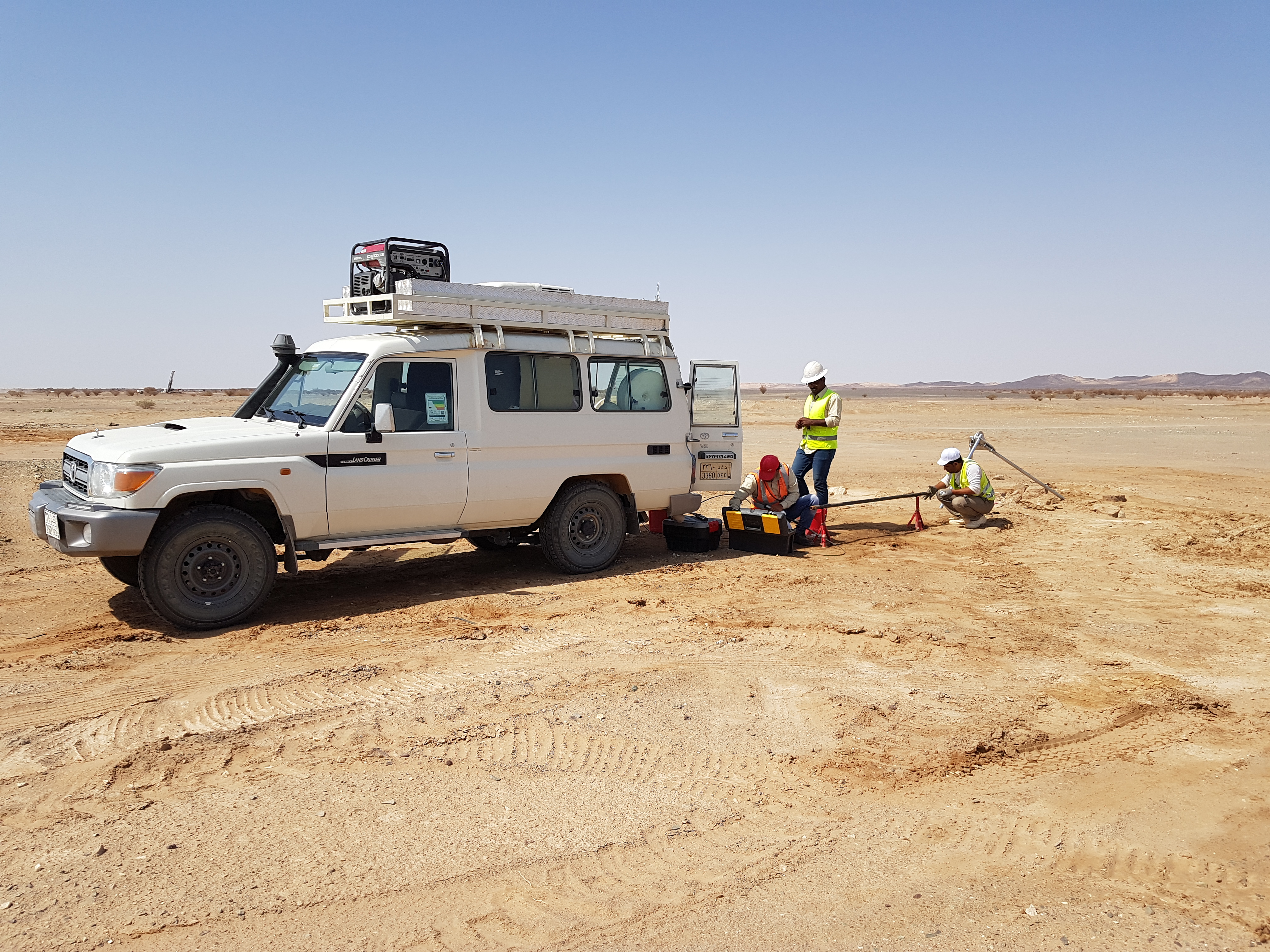
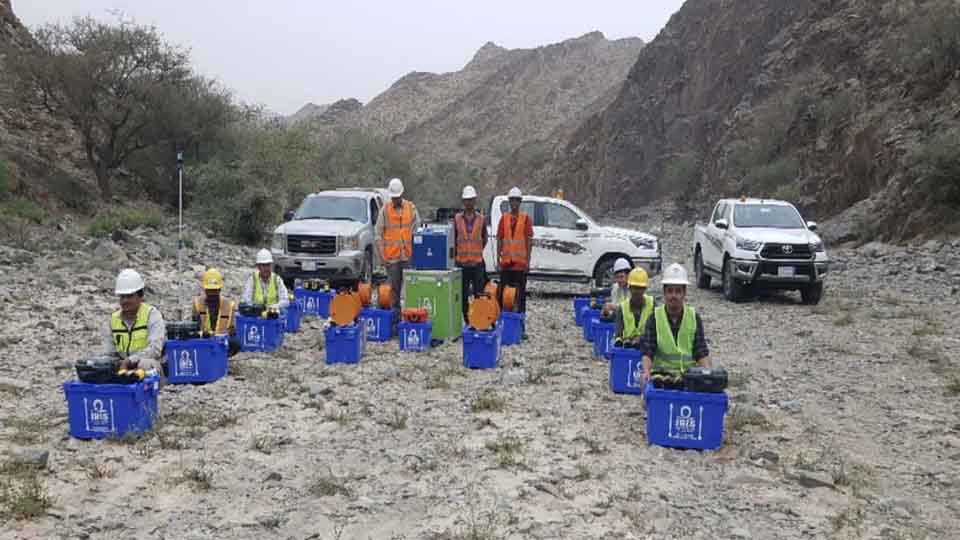
In surveying and mapping we accurately measure and recorde the physical features of land, including boundaries, elevations, and the location of objects. Creating visual representations of the surveyed data, such as maps, charts, and digital models.
GCGC Utilizes various tools like theodolites, levels, GPS receivers, and advance UAV to collect precise data.
Providing raw data and measurements that serve as the foundation for mapping and other applications while producing maps and other visual products that communicate spatial information about the land and its features.
Our Services includes:
1. Boundary Surveys
Determines the exact location of construction site, corners, and boundaries.
Collecting coordinates of the project site and plotting on Civil 3D to help construction designers.
2. Construction Site Surveys
Providing crucial information about the land and existing conditions. They are conducted before, during, and sometimes after construction to ensure accuracy, prevent costly mistakes, and maintain project timelines.
3. Pipeline Route Surveys
Determining the most feasible, safe, and environmentally responsible path for the pipelines. The survey aims to identify and avoid potential hazards such as unstable slopes, seismic zones, flood-prone areas, and culturally sensitive sites
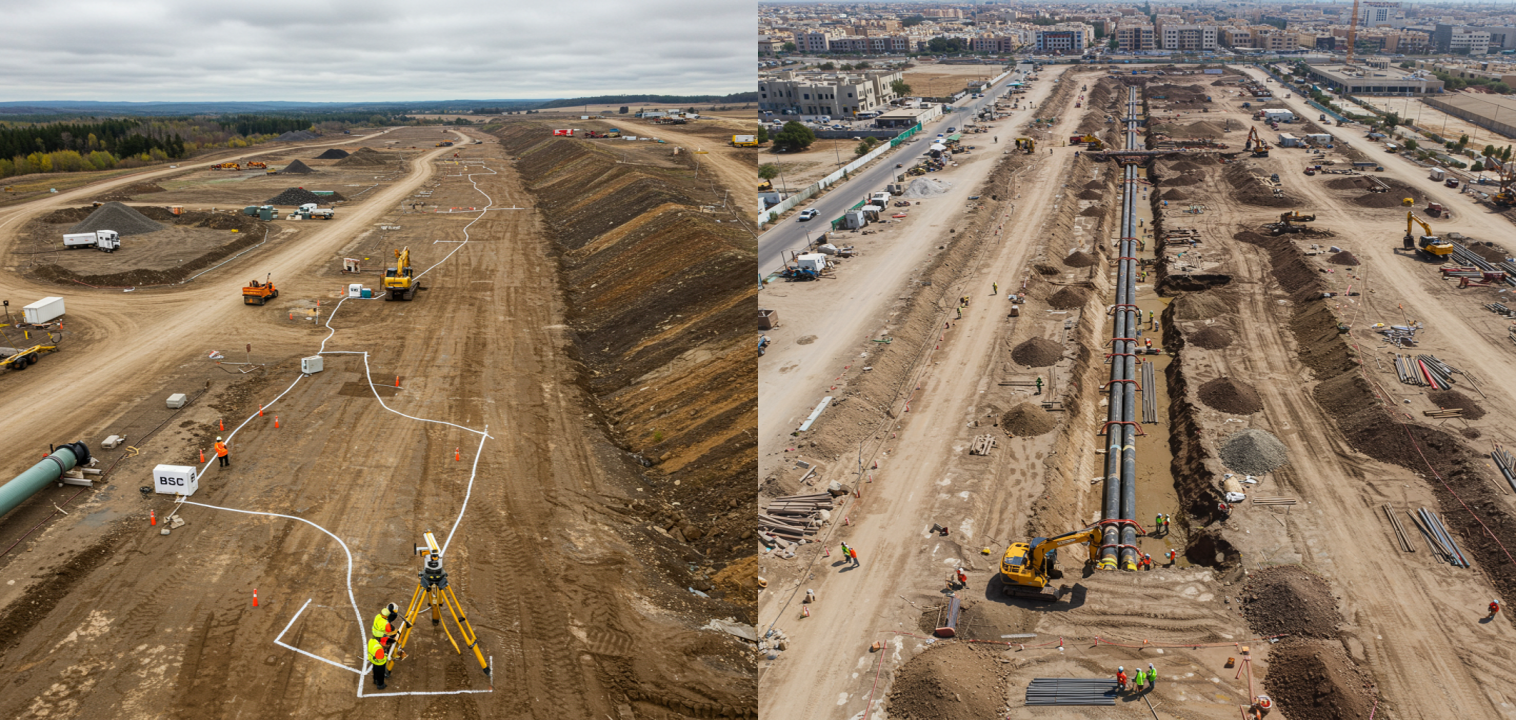

4. Roads and Rail Surveys
Gathering accurate and detailed information about existing roads and rail infrastructure using advanced surveying tools.
5. As Built Surveys
Providing a permanent record of the final location and dimensions of all elements of the project, including buildings, utilities, equipment, and infrastructure. These surveys are essential for future maintenance, repairs, and renovations. Knowing exactly where pipes, wires, and other elements are located prevents costly mistakes during future work.
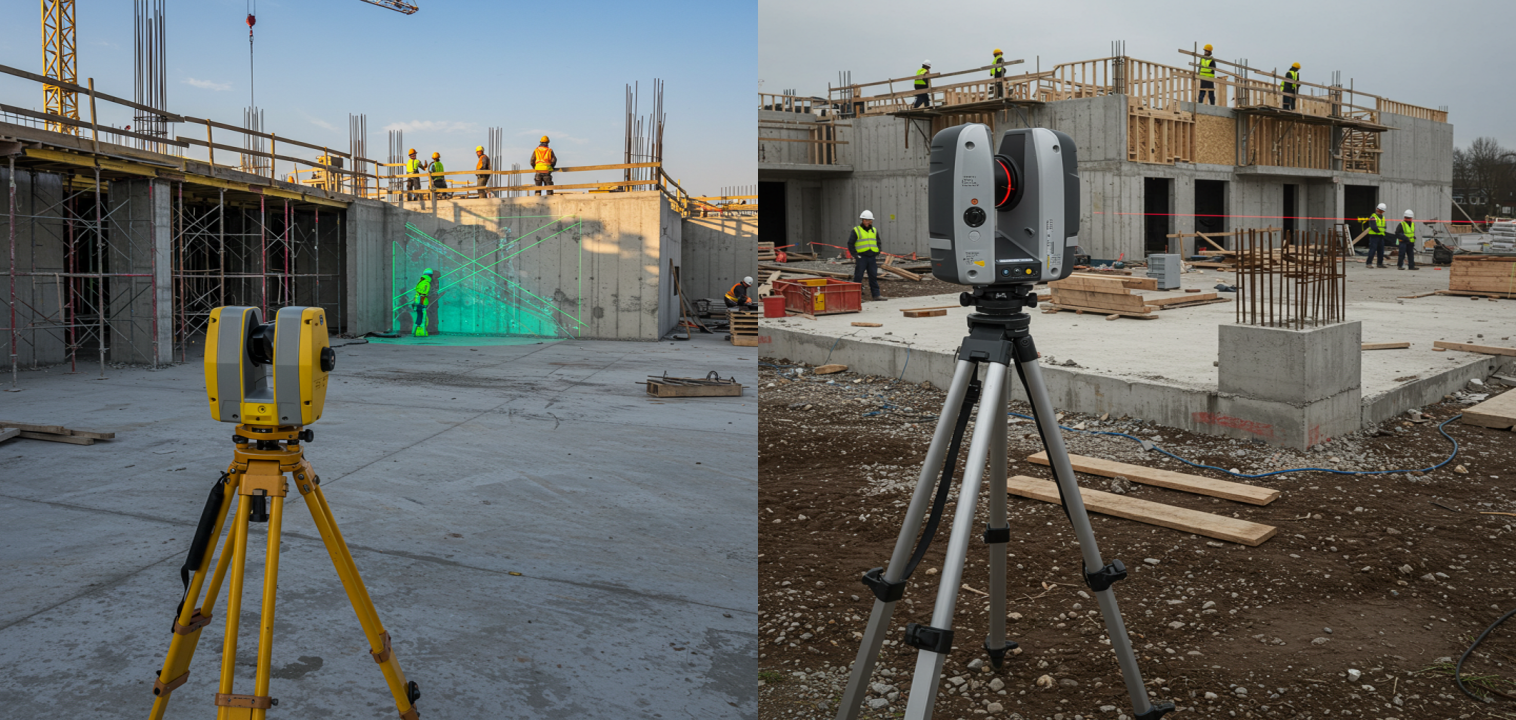
6. Laser Scanning Surveys (3D)
-Creating as-built surveys, documenting existing conditions, and supporting BIM (Building Information Modeling) processes.
-Designing and planning infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and pipelines.
-Documenting and preserving historical buildings and artifacts.
-Quality control, reverse engineering, and creating digital twins of manufacturing facilities.
-Surveying mine sites, monitoring changes, and calculating volumes

Related recommendations
-
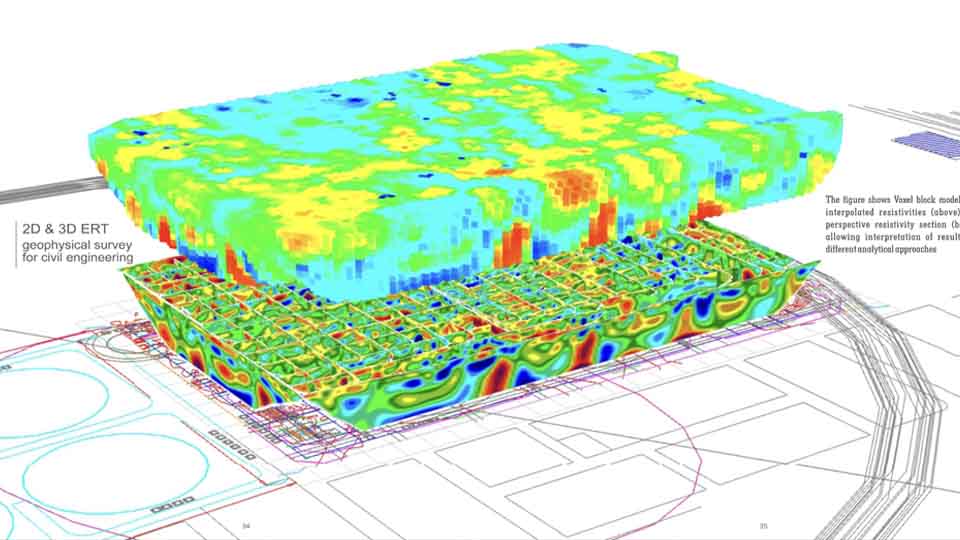
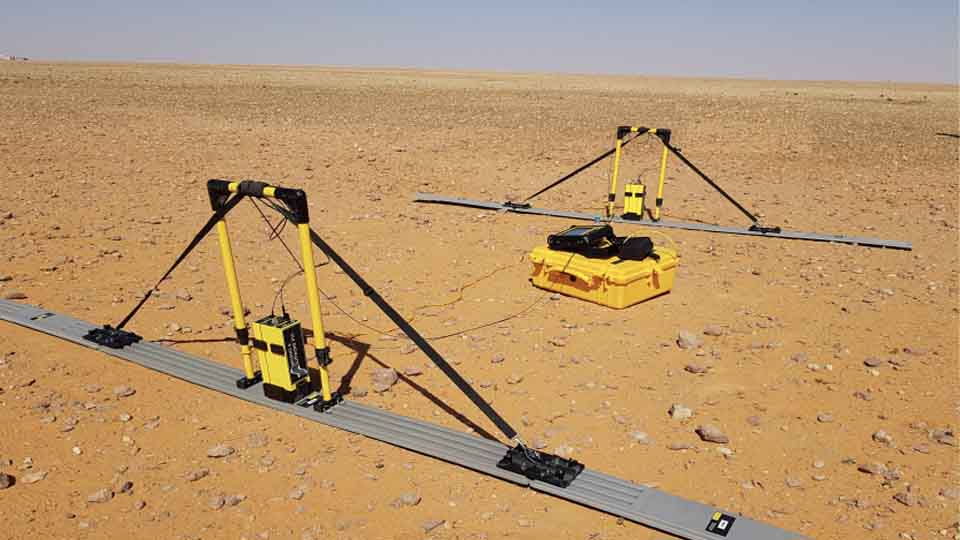
Seismic Methods
Seismic geophysical methods can cost-effectively image the subsurface over a large area and have been extensively used in deep earth studies and natural resource exploration
Learn more -
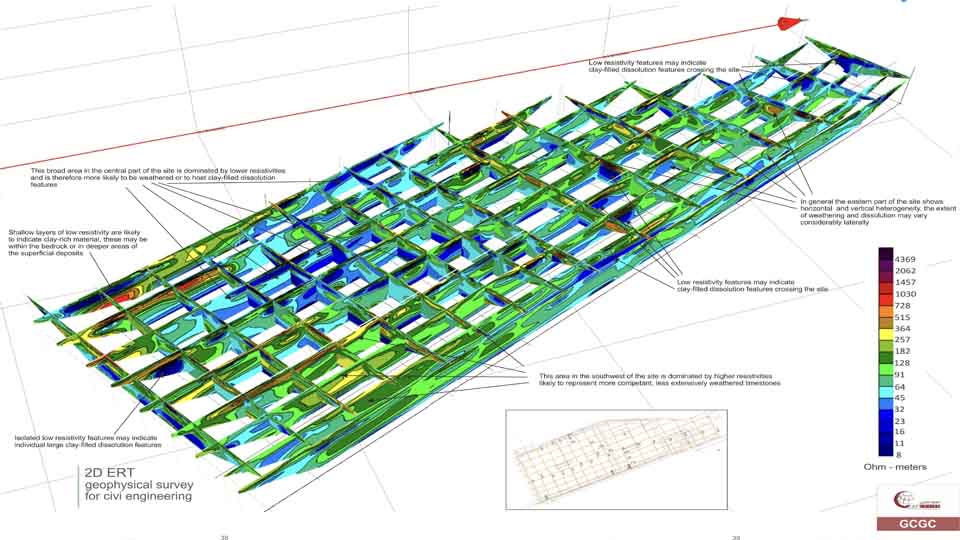
Electrical Methods
The electrical properties of the subsurface vary with the ground material, the presence and saturation level of fluids, and the presence of buried objects. Electrical techniques seek to describe the distribution of these properties as a function of depth and horizontal distance.
Learn more -
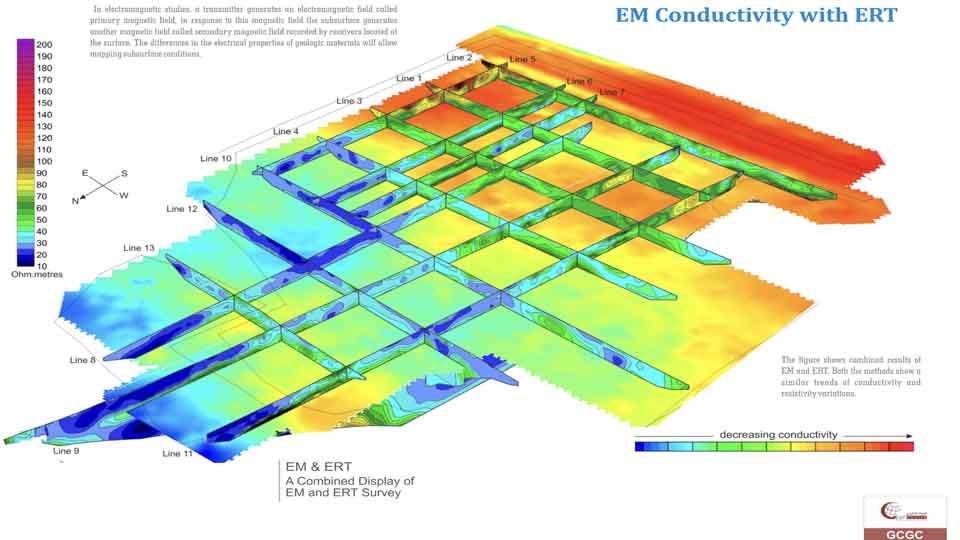
EM Methods
Electromagnetic (EM) surveying, the electrical conductivity of the ground is measured as a function of depth and horizontal distance. Different rocks exhibit different values of electrical conductivity. The electromagnetic method is based on the induction of electric currents in the ground by the magnetic component of electromagnetic waves generated at the surface
Learn more