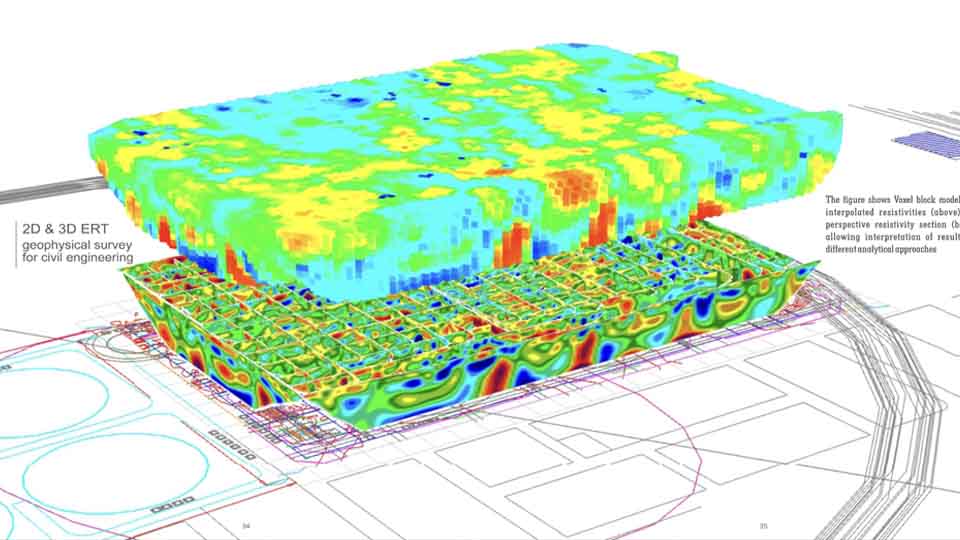
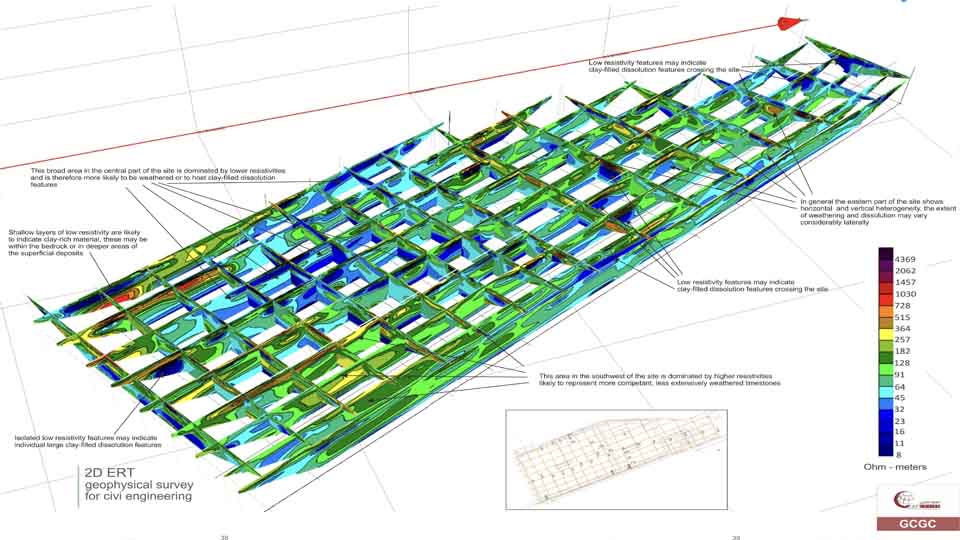
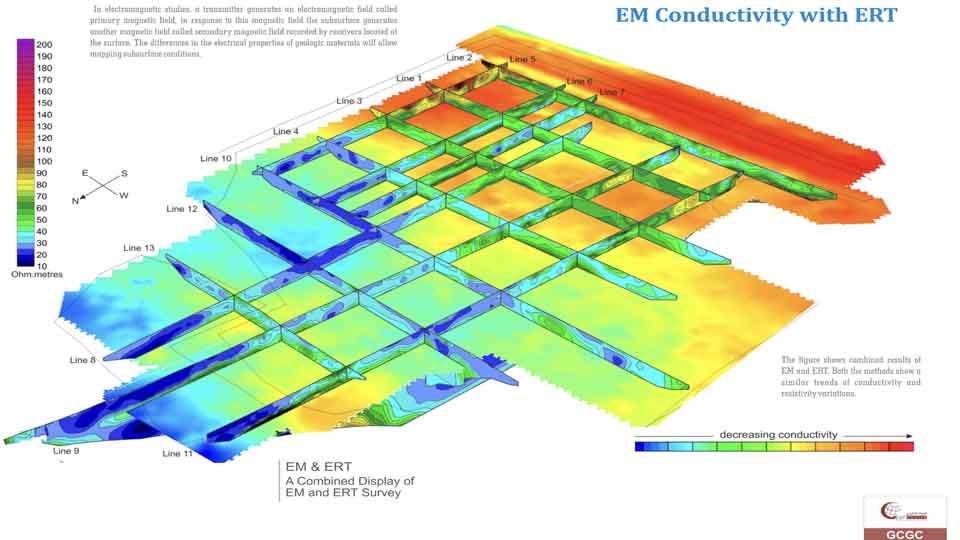
Seismic Methods
Seismic geophysical methods can cost-effectively image the subsurface over a large area and have been extensively used in deep earth studies and natural resource exploration. There are two major classes of seismic waves: body waves, which pass through the volume of a material; and, surface waves, that exist only near a boundary.
1-Seismic Method Involves Following Techniques
2-Seismic Reflection Surveys
3-Seismic Refraction Surveys
4-Multi-Channel Analysis of Surface Waves
5-Horizontal to Vertical Spectral Ratio Analysis (HVSR)
6-Borehole Seismic Surveys
Applications
- Bedrock profiling - Engineering Rock head
- Mapping Geological Layers and Structures
- Water Table Depth
- Rock rippability and quality
- Engineering Parameters: Poisson Ratio, Shear Modulus, Bulk Modulus, P & S wave Velocity
- Mining and subsurface structure delineation
- General Geologic structure and Geologic Layering
- Locating sinkholes and Buried Channels
Techniques
-
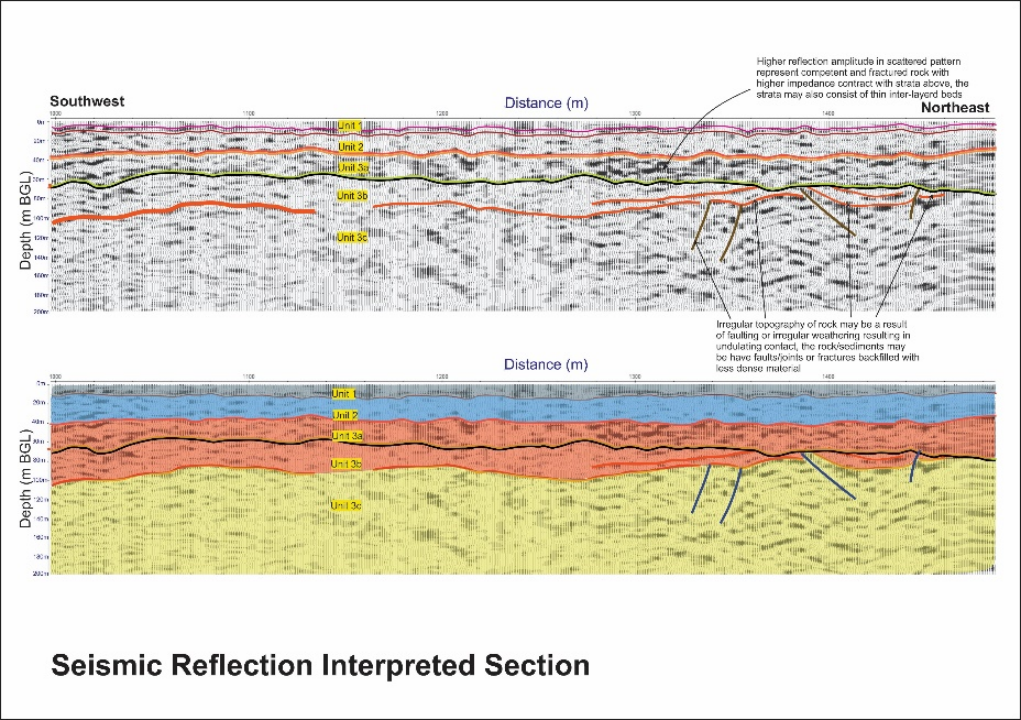
Seismic Reflection Surveys
We use Seismic reflection, a method of geophysical exploration that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite, a specialized air gun or a seismic vibrator, commonly known by the trademark name Vibroseis. -
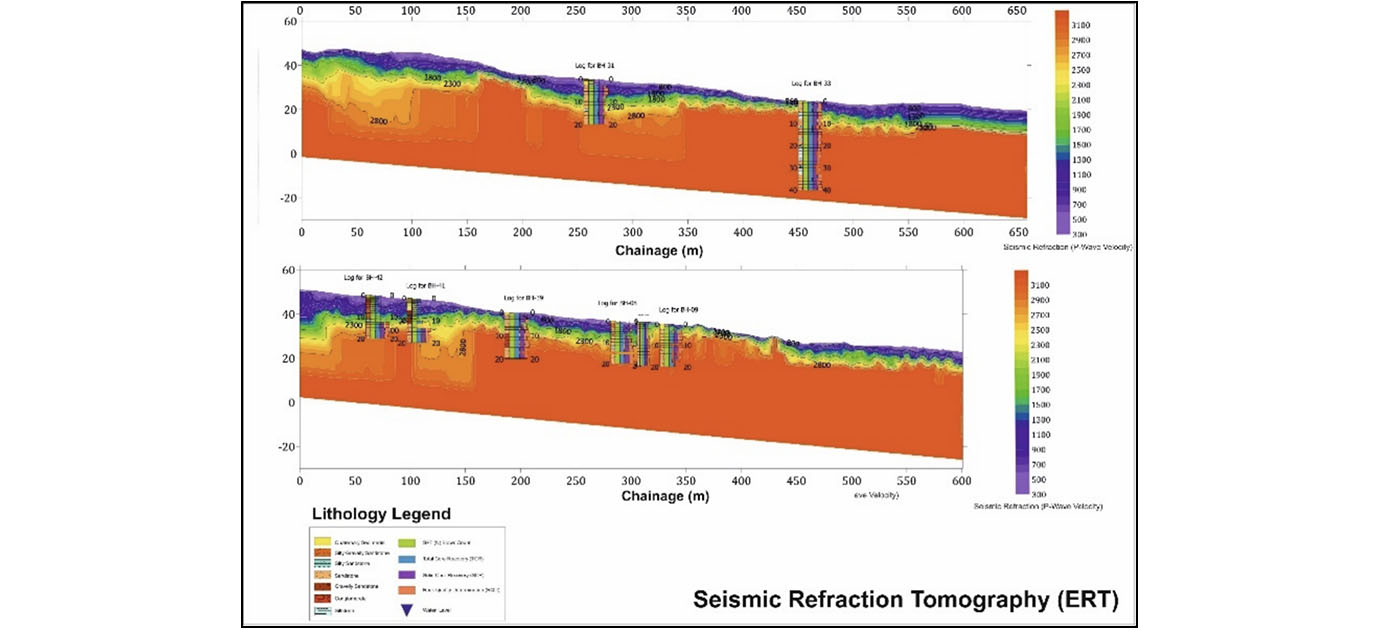
Seismic Refraction Surveys
The seismic refraction method is based on the measurement of the travel time of seismic waves refracted at the interfaces between subsurface layers of different velocity through soil and rock. Seismic refraction remains the preferred method for accurately mapping the depth to competent bedrock under most conditions -
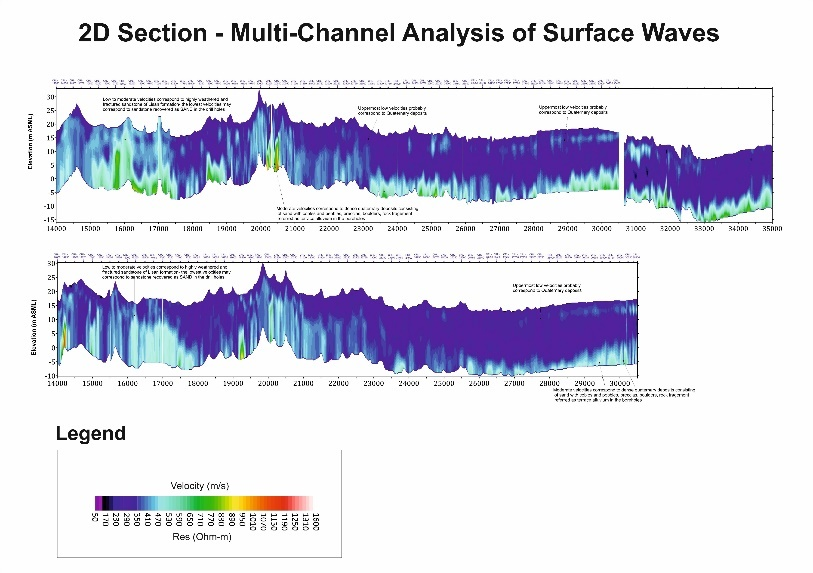
Multi-Channel Analysis of Surface Waves
GCGC offers Multi-channel analysis of surface waves (MASW), a seismic method for the characterization of the shear wave velocity of the subsurface. MASW utilizes the dispersive properties of Rayleigh-type surface waves to determine the variation of shear wave velocity with depth -
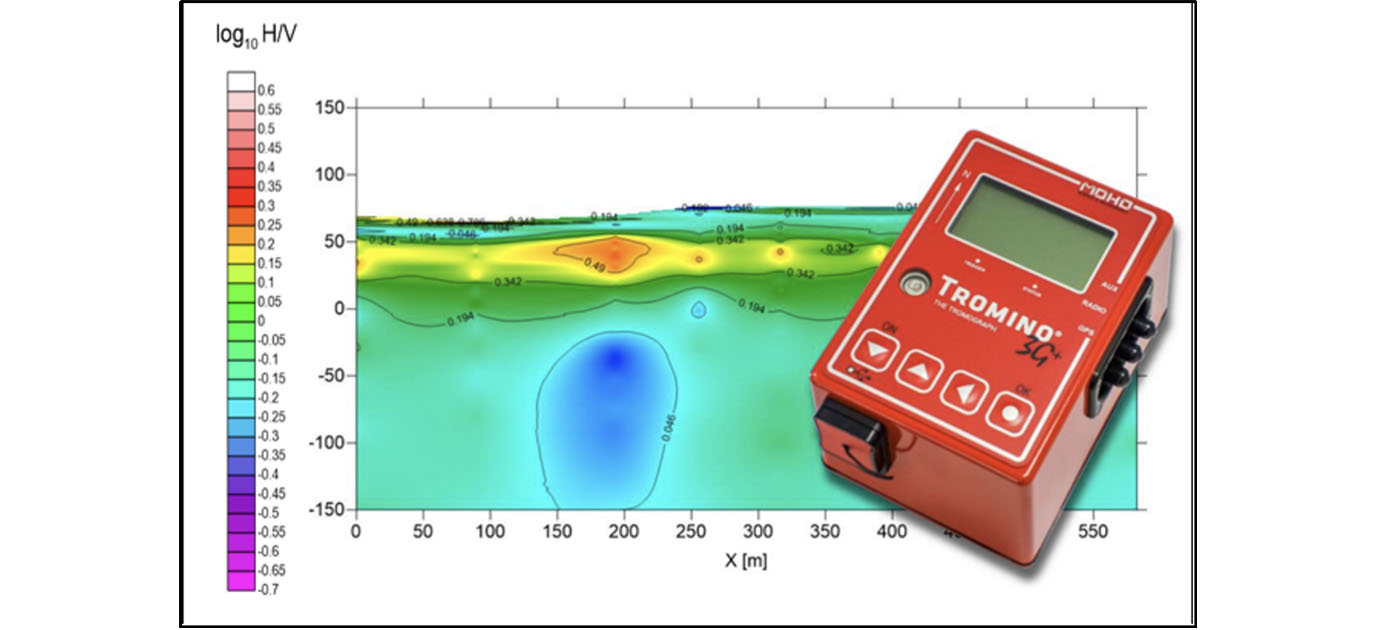
Horizontal to Vertical Spectral Ratio Analysis (HVSR)
GCGC offers HVSR to its client, one of the ideal solution in Engineering Geology - for seismic site effect assessment, estimating VS30, bedrock mapping, seismic stratigraphy and for Civil Engineering – for investigating soil structure interaction, vibration analysis and monitoring damaging the structures -
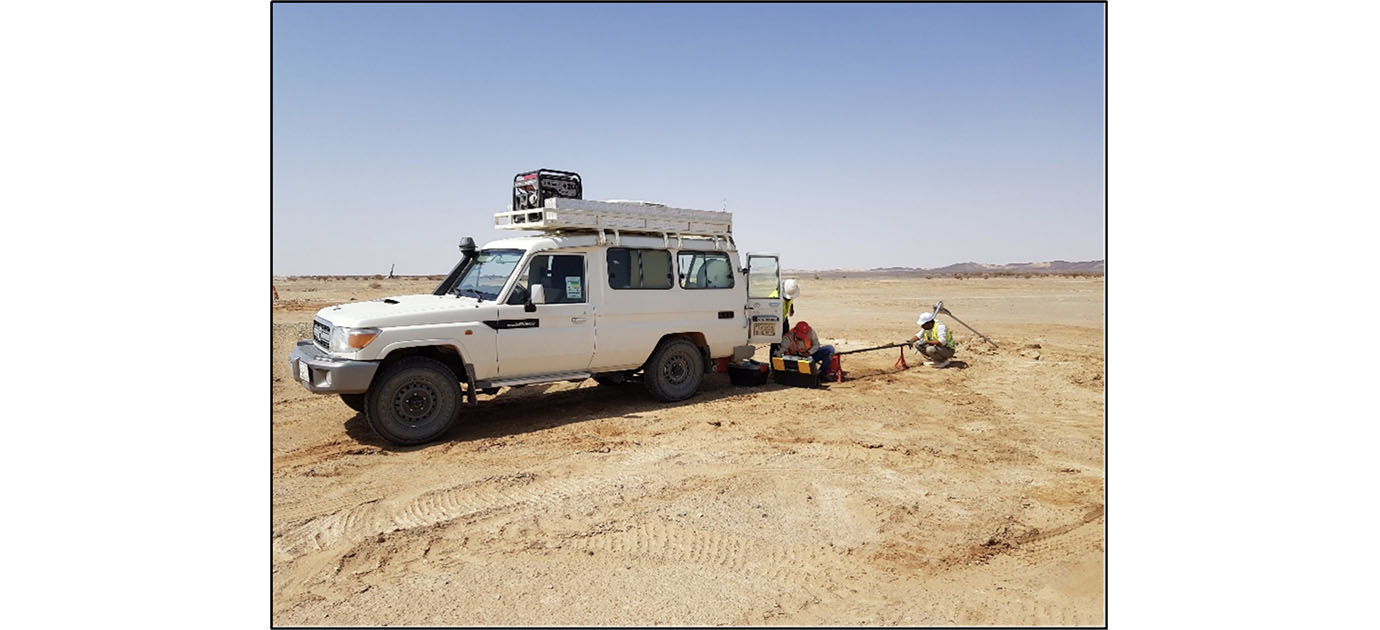

Borehole Seismic Surveys (Downhole & Crosshole)
Down-hole require only a single borehole. Seismic energy is generated on surface at a fixed distance from the top of the borehole. The travel times of the first-arrival seismic waves are measured at regular intervals down the hole. Cross-hole involve measurement of the travel time of seismic energy transmitted between two boreholes. One hole is used to deploy the source whilst the other hole is used to detect the arrival of the seismic energy.