-
Seismic Methods
Seismic geophysical methods can cost-effectively image the subsurface over a large area and have been extensively used in deep earth studies and natural resource exploration
Learn more -

Electrical Methods
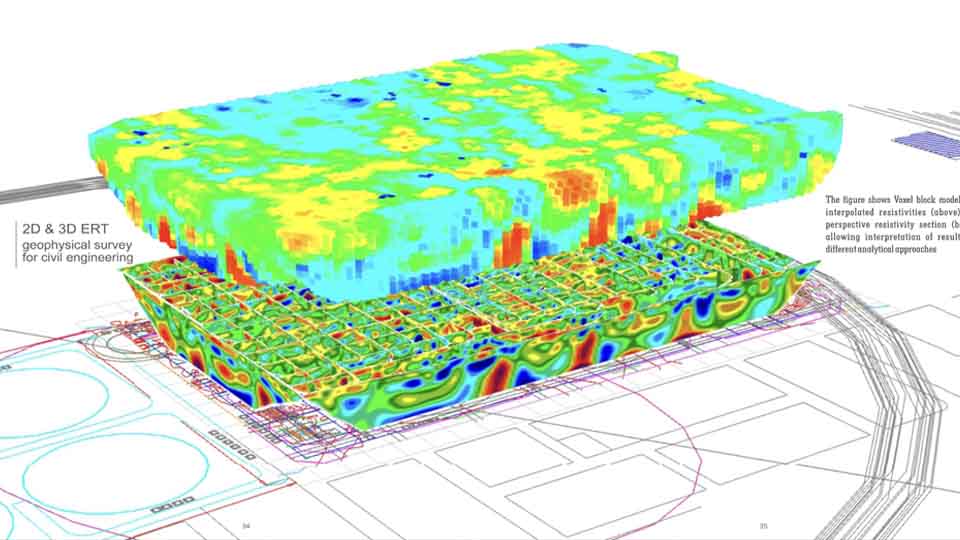
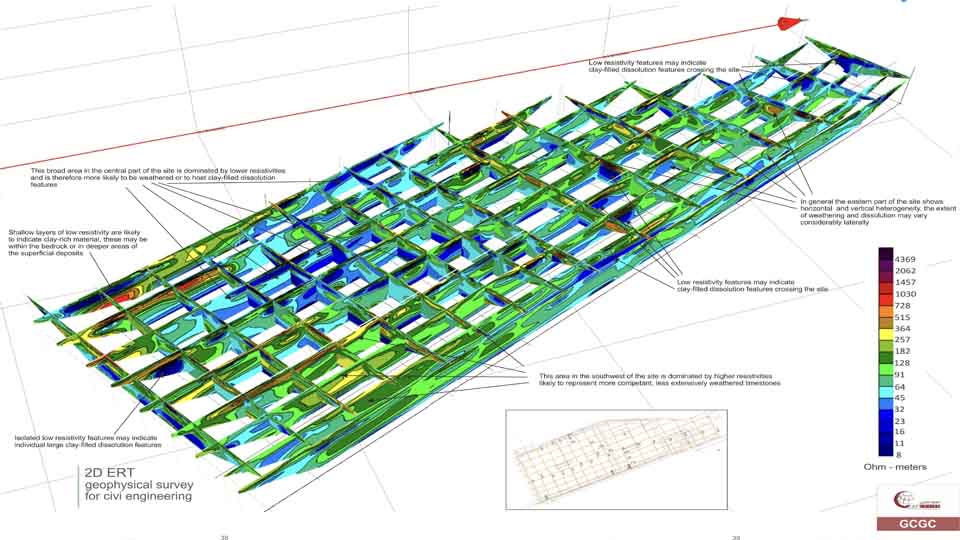
The electrical properties of the subsurface vary with the ground material, the presence and saturation level of fluids, and the presence of buried objects. Electrical techniques seek to describe the distribution of these properties as a function of depth and horizontal distance.
Learn more -
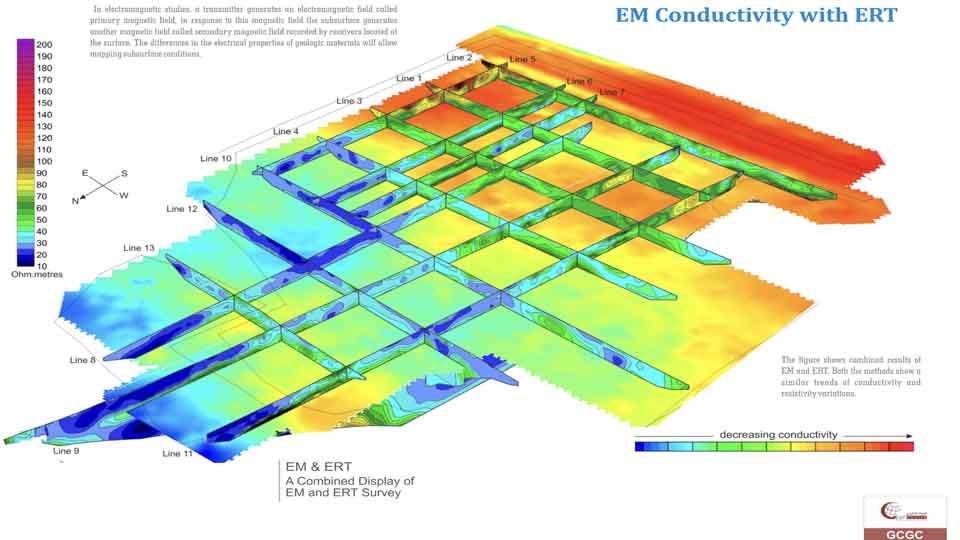
EM Methods
Electromagnetic (EM) surveying, the electrical conductivity of the ground is measured as a function of depth and horizontal distance. Different rocks exhibit different values of electrical conductivity. The electromagnetic method is based on the induction of electric currents in the ground by the magnetic component of electromagnetic waves generated at the surface
Learn more -
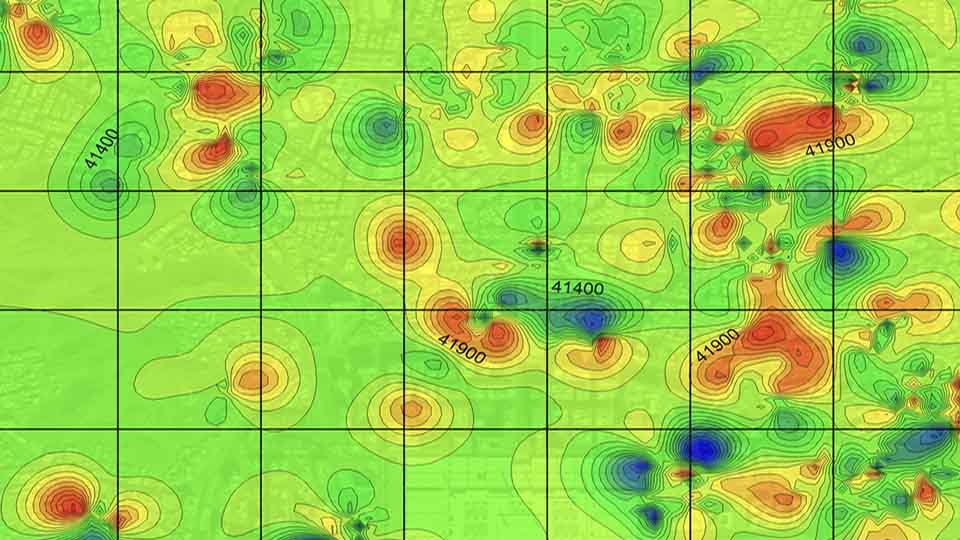
Magnetic Methods
For the magnetic geophysical method to be useful, the targeted geologic structure or man-made item needs to be the right size and orientation to the earth's field such that anomalous field can be detected.
Learn more -
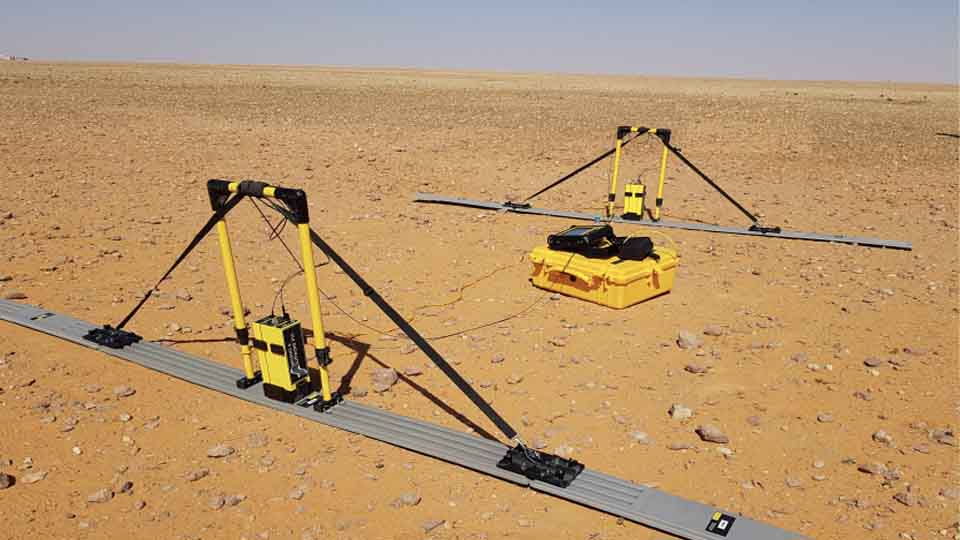


GPR Method
GPR works by sending a tiny pulse of energy into a material and recording the strength and the time required for the return of any reflected signal. A series of pulses over a single area make up what is called a scan.
Learn more -
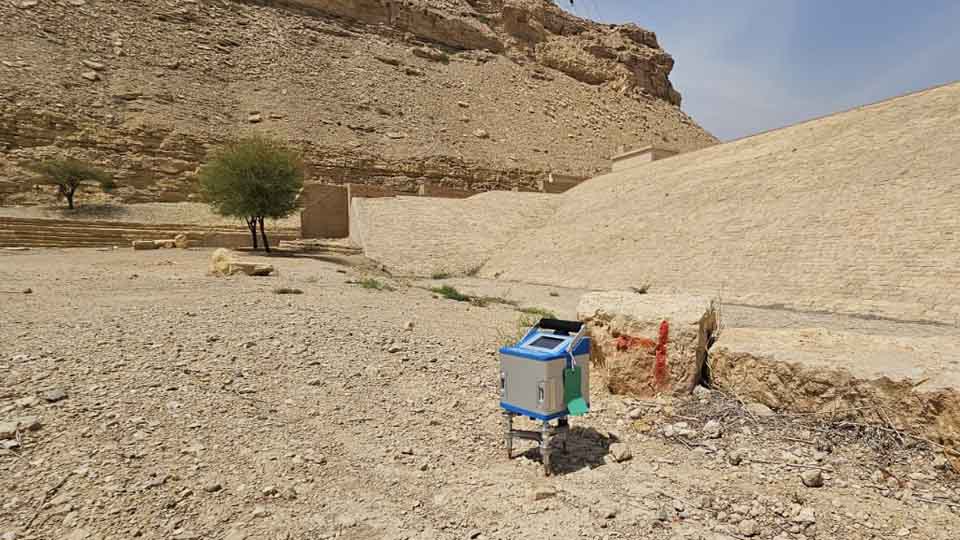


Gravity Methods
The gravity technique is based on measuring localized changes in the Earth's gravitational field which are caused by materials of different densities.
Learn more -
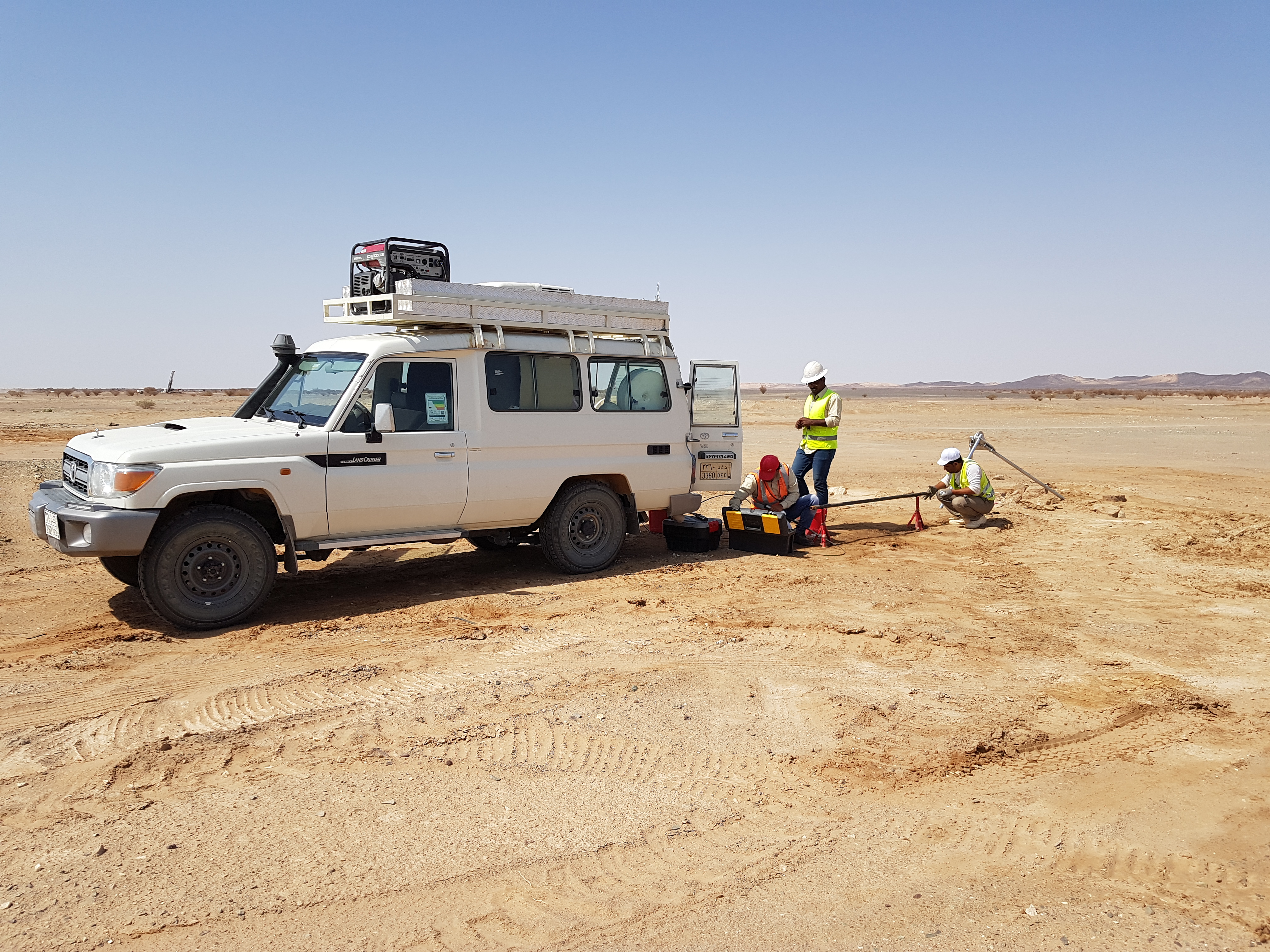


Borehole Logging
Well Logging is an evaluation method in which a logging crew lowers a special tool, a sonde, into the well and then pulls it back up. As the sonde passes the formations on its way up the wellbore, it senses and measures electrical, radioactive, and acoustic (sound) properties of the rocks.
Learn more