GPR Method
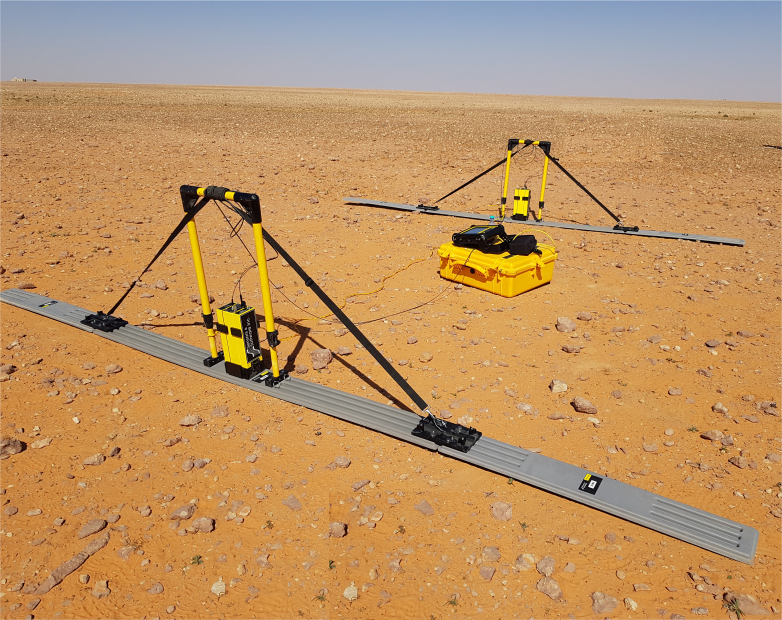

GPR works by sending a tiny pulse of energy into a material and recording the strength and the time required for the return of any reflected signal. A series of pulses over a single area make up what is called a scan. Reflections are produced and the strength, or amplitude, of the reflection is determined by the contrast in the dielectric constants and conductivities of the two materials.
1-High Frequency GPR
2-Low Frequency GPR
Applications
- Utility Locating and Concrete Inspection
- Detection of Voids, Caves and Mines
- Detection of Buried Pipes and Mapping Buried Foundations
- Road Inspection and Railway Evaluation
- Depth to bedrock, Water Table and Geological Mapping
- Mapping Archaeological Features
- Contamination and Landfill Extent Mapping
Techniques
-
High Frequency GPR
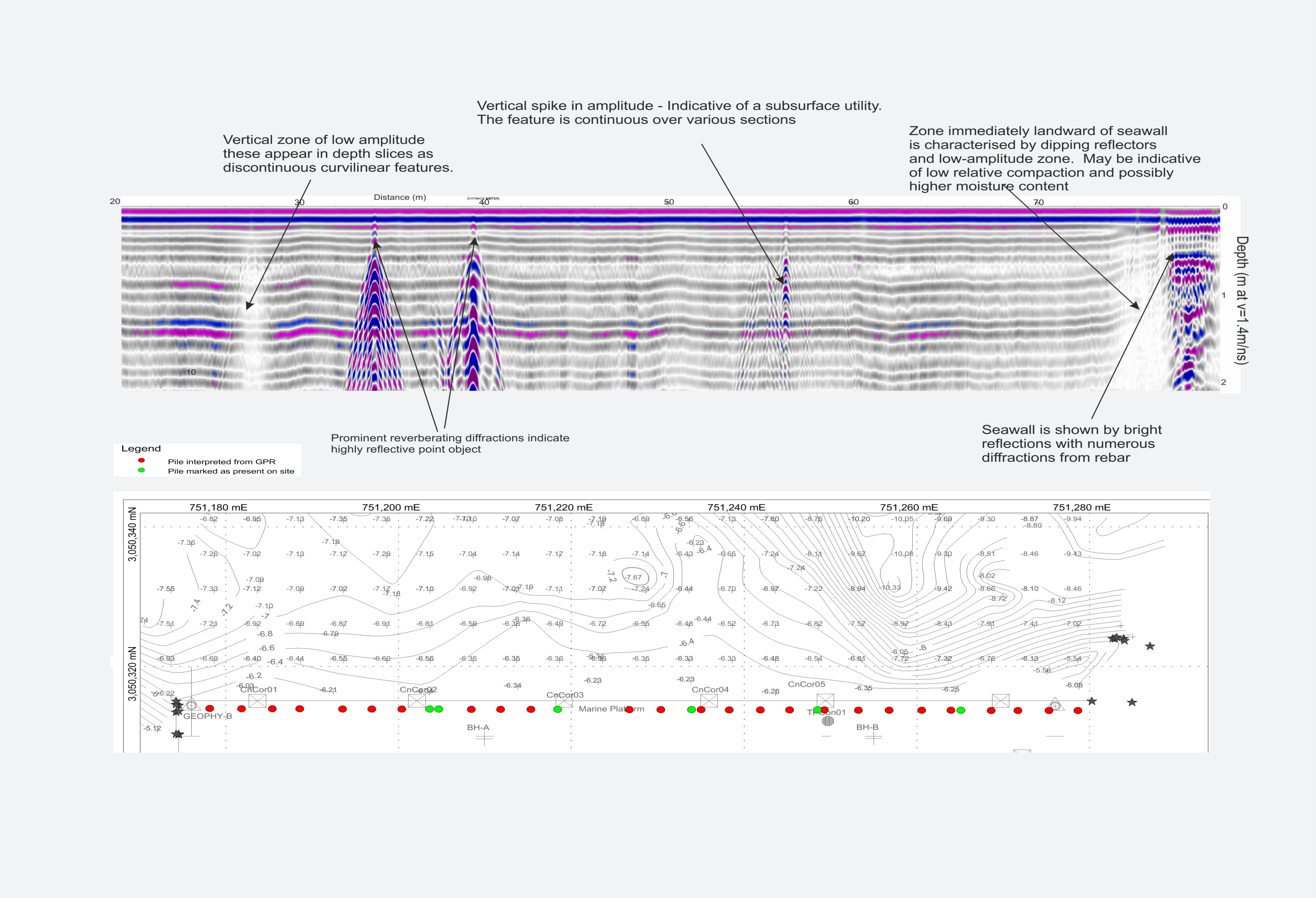
With the wide range of antennae available, the GPR technique can be applied to numerous geological, environmental and engineering applications with investigation depths from a couple of centimeters to up to ~10mbgl. Usually High Frequency GPR are used for utility detections and gives good resolution data up to 4 meters below the ground. -
Low Frequency GPR
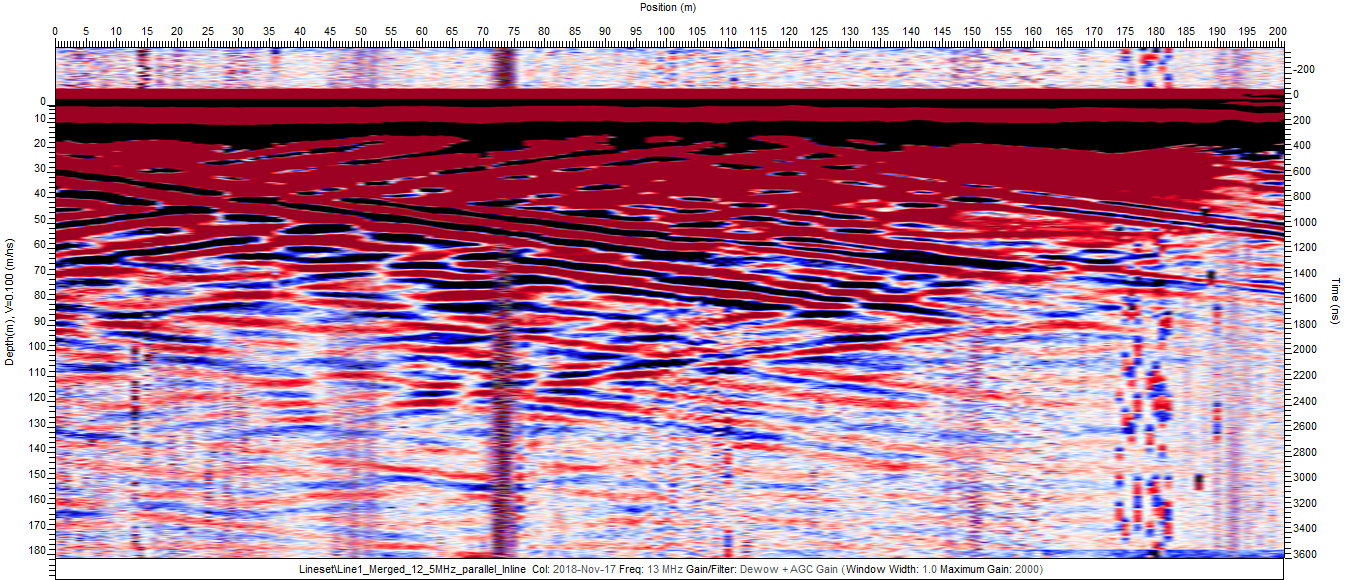
Low frequency antenna are the good tools to locate subsurface fractures, voids and cavities. The data can be collected as a series of 1D soundings, 2D traverses, or in more complex situations as a 3D volume. With this dynamic versatility, the low frequency GPR technique can be applied in a wide variety of circumstances.