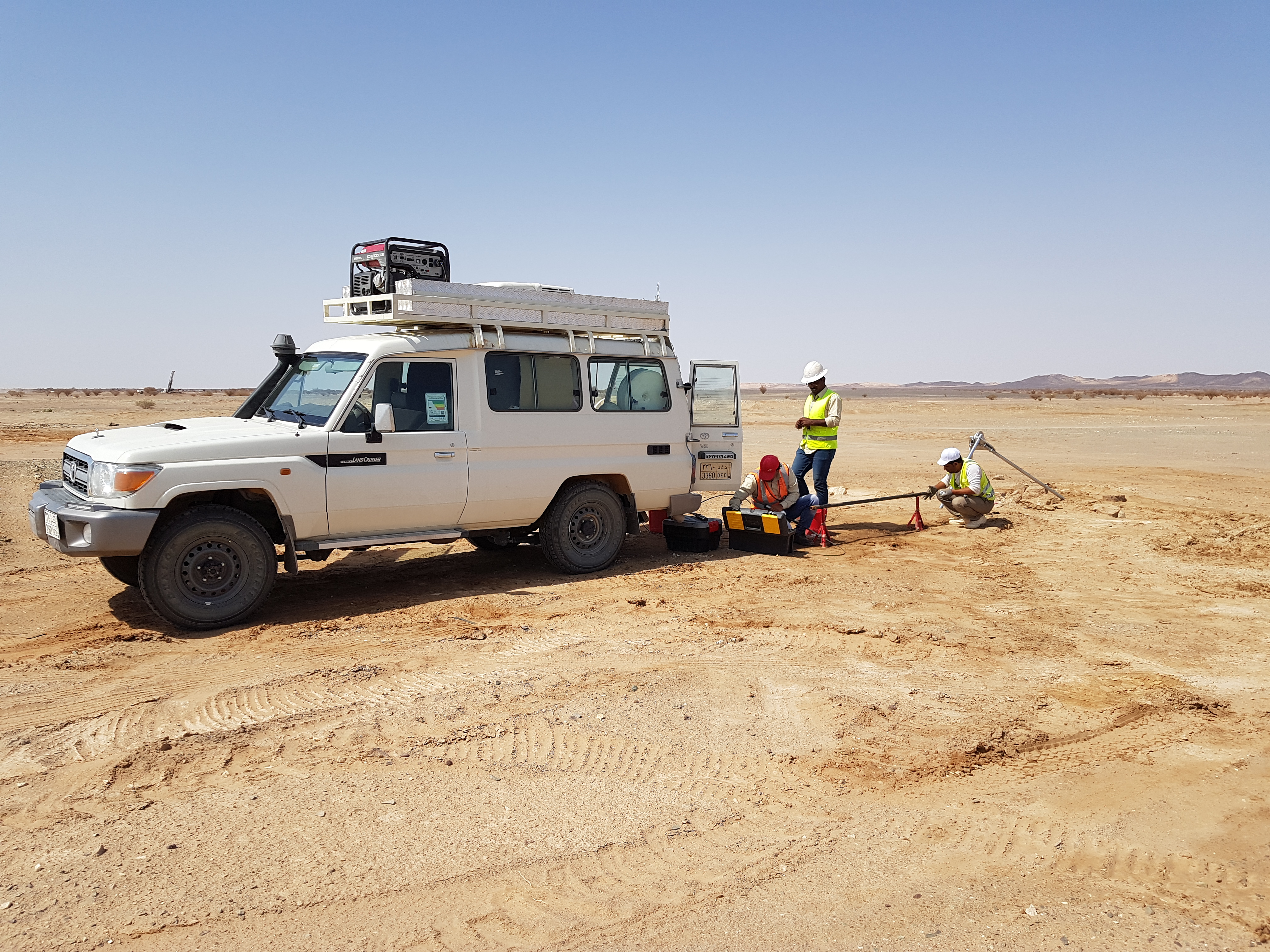
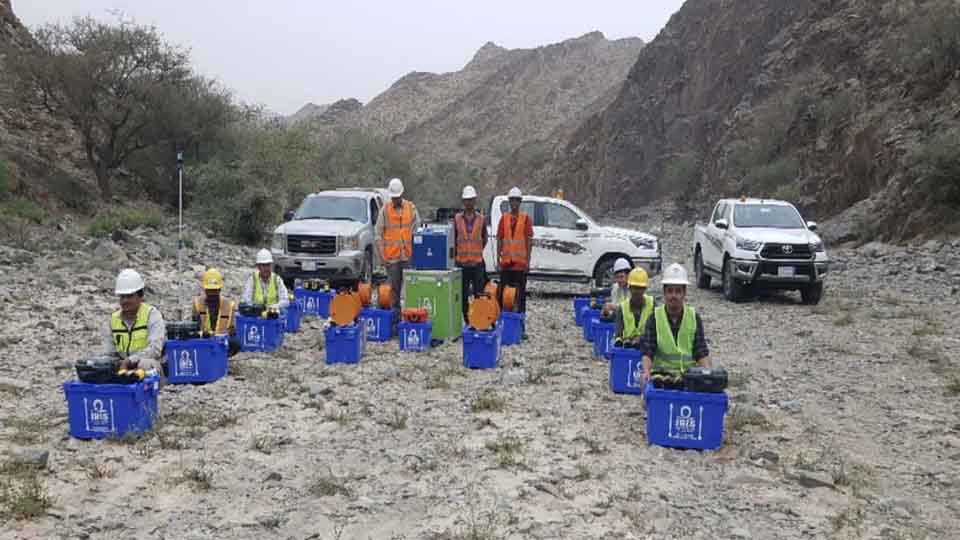
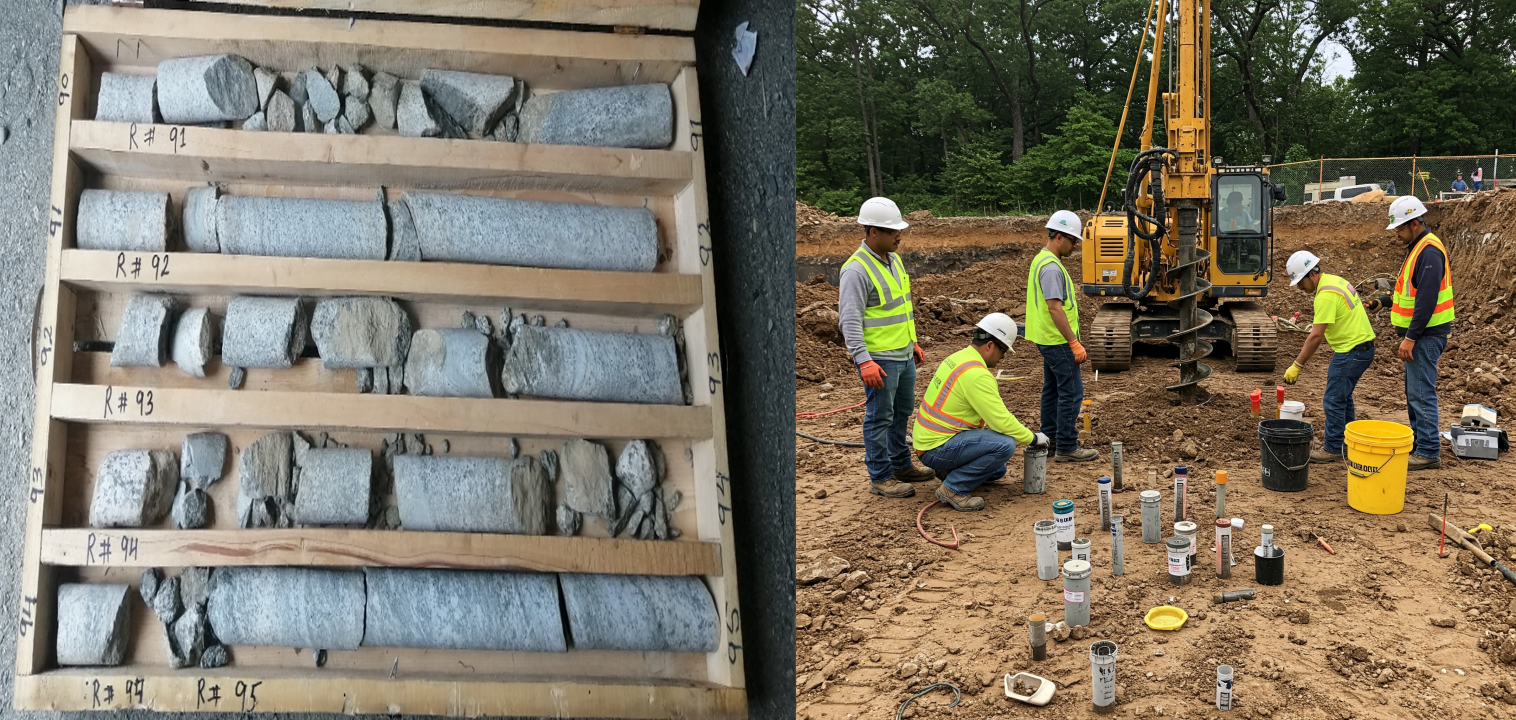
1. Sampling : Collection of disturbed and undisturbed soil, rock, and groundwater samples for further testing in the lab
2. Field Testing : In-situ tests to assess soil strength and other properties, Standard Penetration Test (SPT),
3. Cone Penetration Test(CPT) : to evaluate the subsurface soil properties for engineering and construction purposes.
4. Permeability Tests : to determine the ability of soil to allow fluids to flow through it.
5. Soil and Rock Core Logging : Detailed recording of the subsurface materials encountered during drilling, including soil and rock characteristics.
6. Trial Pits and Trenches: For the visual Inspection
7. Trial Pits and Trenches: Installation of piezometers or other groundwater monitoring instruments to measure water table levels and groundwater conditions.
8. Pressure Grouting: Using grout to fill voids or improve the ground conditions for foundation stability
9. Plate Load Testing: Conducted to evaluate bearing capacity and settlement characteristics of soil under loads.
10. Vibration Monitoring: Monitoring ground and structural vibrations during construction to ensure they remain within safe limits for nearby structures.
11. Construction Monitoring: On-site geotechnical engineers provide continuous monitoring during earthworks, excavation, and foundation construction to ensure compliance with design specifications.
12. Soil and Groundwater Testing: Analyzing soil, rock, and groundwater conditions to evaluate stability, bearing capacity, and potential hazards.

Related recommendations
-
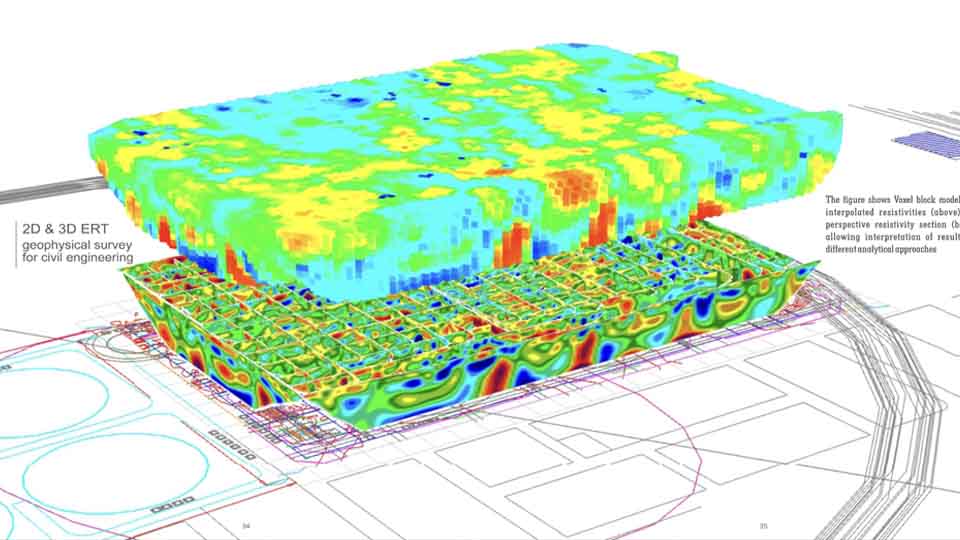
Seismic Methods
Seismic geophysical methods can cost-effectively image the subsurface over a large area and have been extensively used in deep earth studies and natural resource exploration
Learn more -
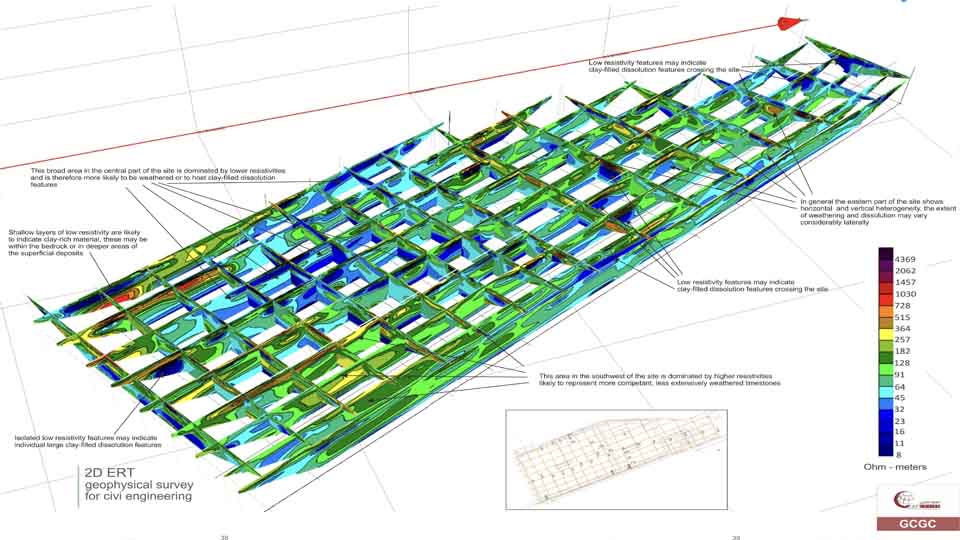
Electrical Methods
The electrical properties of the subsurface vary with the ground material, the presence and saturation level of fluids, and the presence of buried objects. Electrical techniques seek to describe the distribution of these properties as a function of depth and horizontal distance.
Learn more -
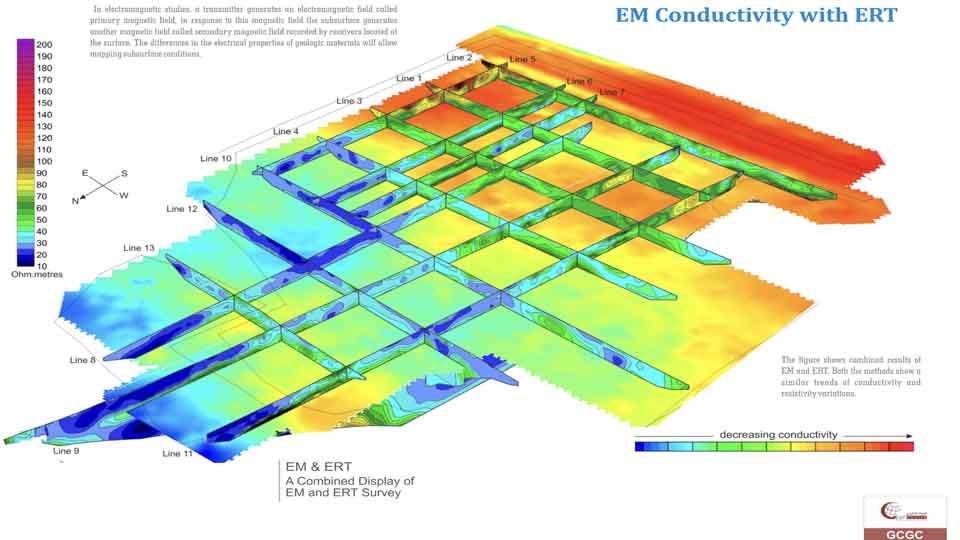
EM Methods
Electromagnetic (EM) surveying, the electrical conductivity of the ground is measured as a function of depth and horizontal distance. Different rocks exhibit different values of electrical conductivity. The electromagnetic method is based on the induction of electric currents in the ground by the magnetic component of electromagnetic waves generated at the surface
Learn more